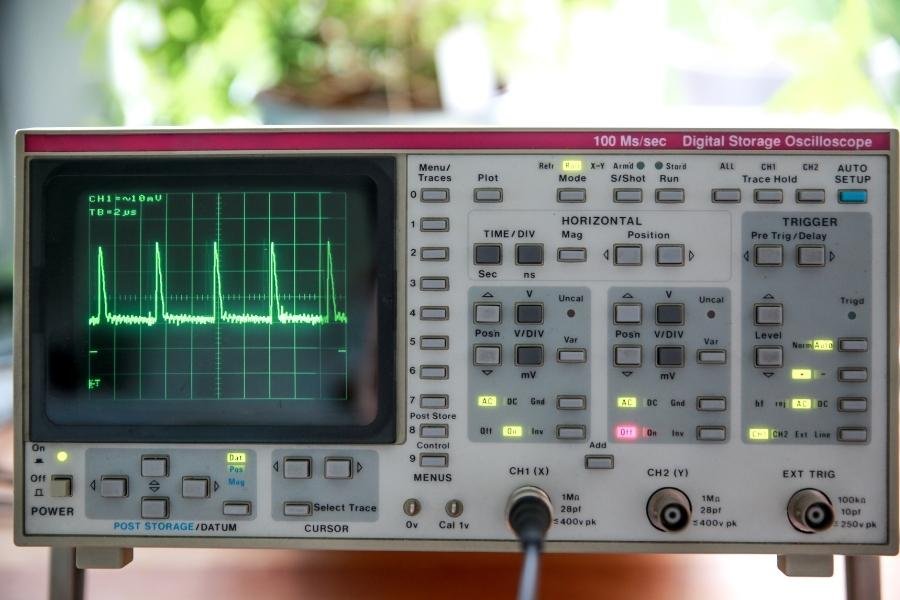
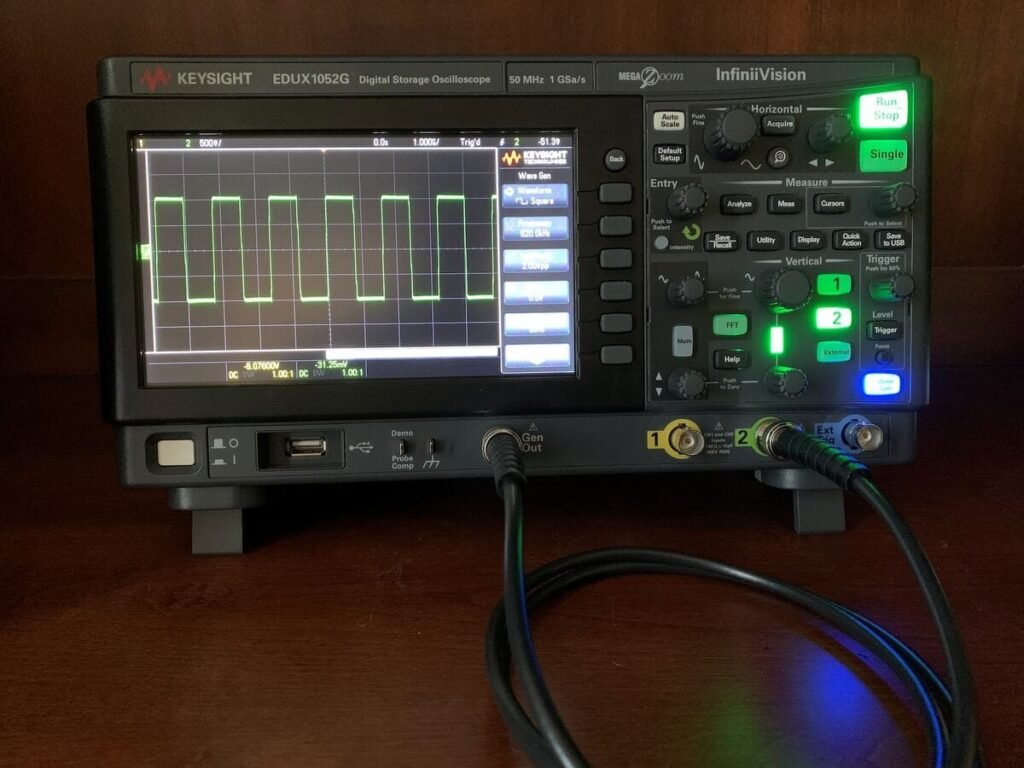
How To Measure Gain On An Oscilloscope under $199 (in 2024)
Oscilloscopes are powerful tools that enable engineers to monitor voltage fluctuations in electrical signals. They’re also one of the most important tools in an engineer’s toolkit and a useful device for measuring gain.






Don’t forget to also peruse our oscilloscopes, spectrum analyzers, and other electronics lab tools.
In this blog post, we will discuss how oscilloscopes measure gain as well as tips on how you can use your oscilloscope to measure gain.
If you would like to learn more about oscilloscopes and their uses, read our blog post about signal analyzers vs oscilloscopes first.

What Is Gain?
Gain is a measure of how much an amplifier boosts the amplitude of a signal. It is often expressed as a ratio of input-to-output voltage or current, and is sometimes used as a synonym for “amplification”.
For example, if an amplifier’s output voltage is 1 V whereas its input voltage is 0.5 V, the gain of the amplifier is 2 (1 V / 0.5 V). This amplifier has a gain of two because it increased the voltage by a factor of two. Therefore, gain is essentially how much the signal is amplified.
Gain is important to understand in the field of electronics because it determines how much an amplifier distorts an input signal. For example, if you have a signal that is 0.5 V and you send it through an amplifier with a gain of 2, the output signal will be 0.5 V × 2 = 1 V, which is an ideal output.
But let’s say you use a signal that is 1 V. Then the output signal will be 1 V × 2 = 2 V. When a signal is amplified too much, it can cause problems like clipping and noise.


How Do Oscilloscopes Measure Gain?
Before we discuss how to measure gain with an oscilloscope, it is important to understand how an oscilloscope measures gain. Oscilloscopes can be used to measure gain in two ways – manually and automatically.
Manual Gain Measurement
In manual gain measurement, you will set the gain (or amplification) of the amplifier manually, and then use the oscilloscope to measure the voltage drop across an input capacitor. This way of measurement can be useful in certain situations, but it is not recommended for general use due to the inaccuracies of the measurement.
Manual gain measurement is a quick way to measure gain, and it can be helpful when making quick measurements between different signals. It is not recommended for routine use due to inaccuracies in the measurement.
Automatic Gain Measurement
Automatic gain measurement is a more accurate way of measuring gain. It works by sending a signal of known voltage through the amplifier and measuring the output voltage with the oscilloscope.
It is important to note that automatic gain measurement is not instantaneous – it takes a few milliseconds. This means that if you want to measure gain, you will have to run the signal for a few ms and then measure the output voltage with the oscilloscope.
Automatic gain measurement is an accurate way to measure gain, and it is recommended for routine use.


Tips On How To Measure Gain With An Oscilloscope

Use a clean signal with no noise
It is important to use a clean signal when measuring gain with an oscilloscope.
If the signal has too much noise, then the oscilloscope might not be able to accurately measure the gain of the amplifier. If you are having trouble getting a clean signal, you can use a signal source to generate a clean signal or you can try reducing the gain of the amplifier to get rid of the noise.
Set the oscilloscope to the correct scale
The scale of the oscilloscope will affect the measurement of gain, so it is important to set the scale correctly. If you are measuring AC voltage, then the oscilloscope should be set to AC volts. If you are measuring DC voltage, then the oscilloscope should be set to DC volts. Also, make sure to set the correct range on the oscilloscope. If you are measuring voltage between 0 and 10 V, then you should set the scale to 10 V.
Use the right type of amplifier
Different types of amplifiers are designed for different applications. Therefore, it is important to use the right type of amplifier for the application that you are measuring gain for. If you are measuring gain for a low-level application, you will want to use a low-level amplifier. If you are measuring gain for a high-level application, then you will want to use a high-level amplifier.


Limitations Of Oscilloscope-Based Measurement Of Gain
Even though oscilloscopes are powerful tools, they do have a few limitations when it comes to measuring gain.
Manual gain measurement is inaccurate
Manual gain measurement is an inaccurate way of measuring gain with an oscilloscope. Therefore, it is recommended that you use automatic gain measurement when measuring gain with an oscilloscope.
Automatic gain measurement takes time
Automatic gain measurement is an accurate way to measure gain, but it takes time to perform. Therefore, if you want to measure gain quickly, then oscilloscopes might not be your best option.
Oscilloscope bandwidth is limited
The bandwidth of an oscilloscope is limited, which means it might not be able to accurately measure high-frequency signals. Therefore, you should use a low-frequency signal (such as something between 50 Hz and 500 Hz) when measuring gain with an oscilloscope.
The oscilloscope must be set up properly
It is important to set up the oscilloscope properly when measuring gain with it. If you are measuring gain for an AC signal, then you should use an AC coupling capacitor. If you are measuring DC gain, then you should use a DC coupling capacitor. It is also important to set the trigger type and level, the vertical sensitivity, the horizontal sensitivity, and the time base.
Amazon Review Feedback on How To Measure Gain On An Oscilloscope under $199
Measuring gain on an oscilloscope under $199 is surprisingly straightforward and effective, even with budget-friendly models. To measure gain, you’ll need to input a known signal into your device under test (DUT) and compare it to the output signal. First, connect your signal generator to both the DUT input and one oscilloscope channel. Then, connect the DUT output to another oscilloscope channel. Set both channels to the same volts/division and ensure your time base allows you to see several cycles of the waveform. Adjust your signal generator to provide a clean sine wave at an appropriate frequency for your DUT. Measure the peak-to-peak voltage of both the input and output signals using the oscilloscope’s measurement functions. The voltage gain is simply the ratio of output voltage to input voltage. For accuracy, repeat this process at different frequencies within your DUT’s operating range. Most oscilloscopes in this price range offer cursor measurements and basic math functions, which can further simplify the process. While these budget scopes may lack the advanced features of more expensive models, they are more than capable of providing accurate gain measurements for most hobbyists and educational purposes. The key is to understand your oscilloscope’s limitations and to take care in setting up your measurements properly.
Reviewer Final Comments
Gain is a useful measurement to know when dealing with any type of amplifier. Oscilloscopes can be used to measure gain, but they do have a few limitations. When measuring gain with an oscilloscope, it is important to use a clean signal, set the scale correctly, use the right type of amplifier, and set up the oscilloscope properly.