Analog vs Digital Oscilloscopes under $179 (in 2024)
The oscilloscope is a graphic display instrument in which you can see the electrical signals and their variations over time.
According to its internal operation, the oscilloscopes can be analog or digital. Think of a wristwatch. Very similar to an analog watch and a digital watch. The analog version is a more mechanical representation of the internal operations, whereas a digital version is completely made of solid-state digital electronics (which ultimately means, smaller, cheaper, faster, and better).





Don’t forget to also peruse our oscilloscopes, spectrum analyzers, and other electronics lab tools.

Types Of Oscilloscopes
As with the vast majority of measuring equipment, analog and digital oscilloscopes each have their advantages and disadvantages. However, unlike other electronic equipment, the analog oscilloscope does not lose its validity since it is ideal when you want to observe rapid variations of the input signal in real-time.
In other words, it preserves the essence of the original signal (lacks any distortion components, and is why analog vinyl music is loved by music listening experts).

Analog Oscilloscope
These units work directly with the applied signal (in other words mimicking the natural analog world). The signal, once amplified, deflects a beam of electrons vertically, proportional to its value. Work with continuous variables.
However, the main disadvantage is that to observe a stable trace a periodic signal is required since it is such periodicity that allows the formation of the trace. On the other hand, if the signal is too slow, no trace is formed. In the best case, a point is seen, as in radars.
Analog oscilloscopes are considered “the old” versions. Today digital oscilloscopes are much superior and at amazing prices. All in all, analog oscilloscopes are considered by the pros as obsolete.


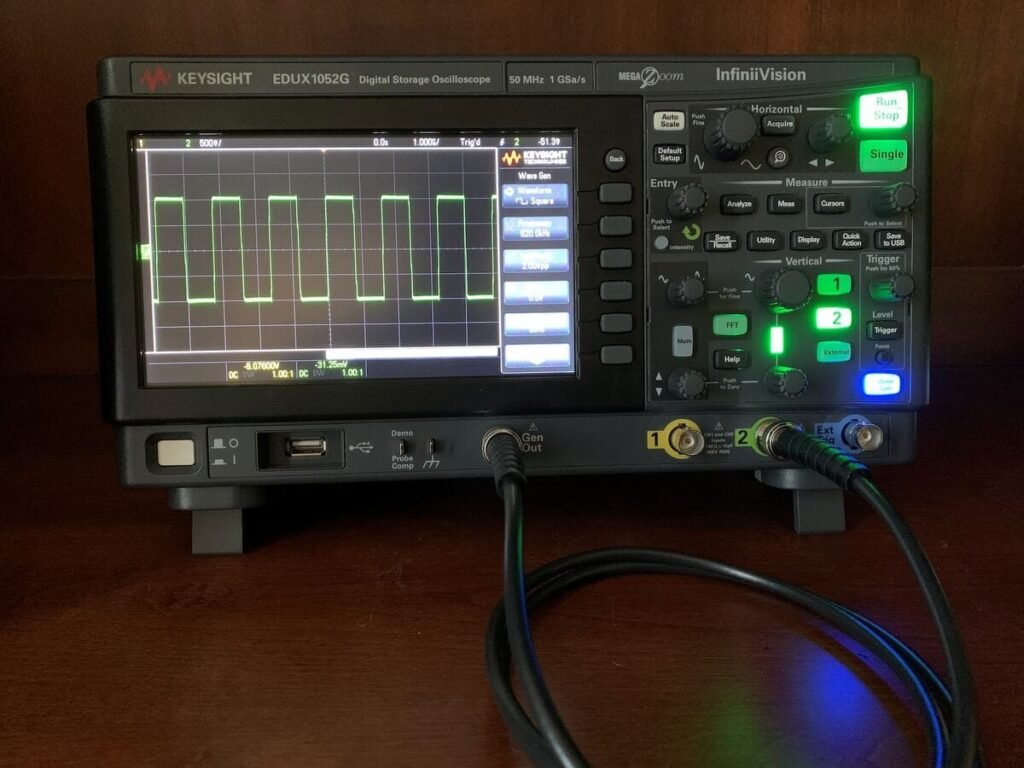
Digital Oscilloscope
A digital oscilloscope is the superior choice. These units became popular in the early 2000s. In the 90’s when I was studying for my electronic engineering degree, all we used was analog oscilloscopes. In the 2000s, everybody and their dogs switched to digital oscilloscopes.
They use an analog-digital converter to digitally store and manipulate the input analog signal. Subsequently, the analog sampled signal is reconstructed on the screen. Digital is preferable when the measurement is made on non-repetitive events, such as voltage peaks that occur randomly. Moreover, the signals can be manipulated on demand with various mathematical algorithms and filters for advanced signal processing.

Digital Phosphor Oscilloscope
This is one of the cases in which it is possible to obtain the best of both worlds: the digital phosphor oscilloscope combines the best of the analog and digital oscilloscope, combining the characteristics of both.
A Digital Phosphor Oscilloscope (DPO) is an advanced instrument that merges digital signal processing with a phosphor screen display. It captures electrical waveforms digitally, utilizing phosphor-like effects to visualize them on-screen. DPOs offer precise waveform analysis, triggering capabilities for event capture, and a range of analysis tools such as FFT. They provide a user-friendly interface for controlling settings and are essential tools for diverse electrical and electronic applications, from research to troubleshooting and quality control.


Oscilloscope Utility
Incredible as it may seem, oscilloscopes have multiple uses: from a doctor to a TV repair technician, you can conveniently use this viewing instrument.
Electrical engineers: They use oscilloscopes for designing, testing, and troubleshooting electronic circuits.
Automotive technicians: Oscilloscopes help diagnose and repair vehicle electronic systems like ignition and fuel injection systems.
Physicists: They utilize oscilloscopes in experiments to measure and analyze electrical signals in various scientific research fields.
Audio engineers: Oscilloscopes aid in analyzing and troubleshooting audio equipment, ensuring optimal performance and quality.
Aerospace engineers: They employ oscilloscopes to test and verify the functionality of electronic systems in aircraft and spacecraft.
What Does An Oscilloscope Do?
With the oscilloscope, you can:
- Detect and find a circuit defect.
- Determine the noise of the signals and how long they last over time, good to determine parameters such as signal-to-noise ratio known as SNR.
- Measure the phase between two signals.
- Determine the period and voltage of a signal.
- Determine, indirectly, the frequency of a signal.
- Determine which part of the signal refers to alternating current (AC) and which part to direct current (DC).
- Debugging signals to find noise sources for example.
- Visualizing and characterizing the rise and decay times of digital signals.
- Undertake logic debugging by looking at multiple signals and characterizing “firing” times and logic sequences.


How To Use An Oscilloscope Correctly
Before making any measurement it is necessary to make the following basic settings:
Check the size of the voltage signal, that is, attenuate or amplify said voltage, for this, you must use the AMPL command.
Adjust the timebase (the oscilloscope measures the voltage determined in a given time cycle). In the case of having repetitive signals, the ideal will be that at least two cycles can be observed on the screen.
Stabilize repetitive signals as well as possible.

Top 10 Oscilloscope Accessories You Must Have?
For any amateur technician or pro, the top 10 oscilloscope accessories required are:
- Probes: Essential for connecting the oscilloscope to the circuit under test, probes come in various types such as passive, active, differential, and high-voltage probes.
- Probe Calibration Equipment: Calibration fixtures or calibration signals ensure the accuracy of oscilloscope measurements by calibrating the probes and compensating for signal distortion or attenuation.
- Logic Analyzer Probes: Crucial for debugging and troubleshooting digital circuits, logic analyzer probes allow oscilloscopes to capture and analyze digital signals effectively.
- Current Probes: Specialized probes designed to measure the electrical current flowing through a conductor without breaking the circuit, particularly useful for troubleshooting power electronics and high-current applications.
- BNC Cables and Adapters: Used to connect various accessories to oscilloscopes, such as signal generators, function generators, or external triggering sources, ensuring versatility in instrument connectivity.
- Attenuators: Help reduce signal amplitudes to prevent damage to the oscilloscope input circuitry when measuring high-voltage signals, ensuring safe and accurate measurements.
- Power Supply: A reliable power source is essential for powering the oscilloscope and other accessories during fieldwork or bench testing, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
- Oscilloscope Probing Accessories Kit: Includes various accessories such as grabbers, hooks, ground leads, and adjustment tools, enhancing flexibility and convenience during measurements.
- EMI/RFI Shielding Enclosures: Shielding enclosures protect sensitive measurements from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI), ensuring accurate readings in noisy environments.
- Oscilloscope Cart or Bench Mount: Provides a stable and ergonomic platform for the oscilloscope, accessories, and other equipment, enhancing convenience and organization in the laboratory or workspace.
How Much Does An Oscilloscope Cost?
(and a recommended starter model)
Analog oscilloscopes are usually tabletop, therefore, they are medium-sized devices. Its price can range between 400 and 1,500 euros, while digital models, both those that are portable and those that are not, are smaller and have a cost that can be between 200 and 1000 euros, depending on their capacity of storage.
When buying an oscilloscope, it is always good to verify the bandwidth, the rise time, the vertical sensitivity, the speed, and the accuracy in the gain and in the base of the times, aspects that will allow to compare the different capacities of the device.
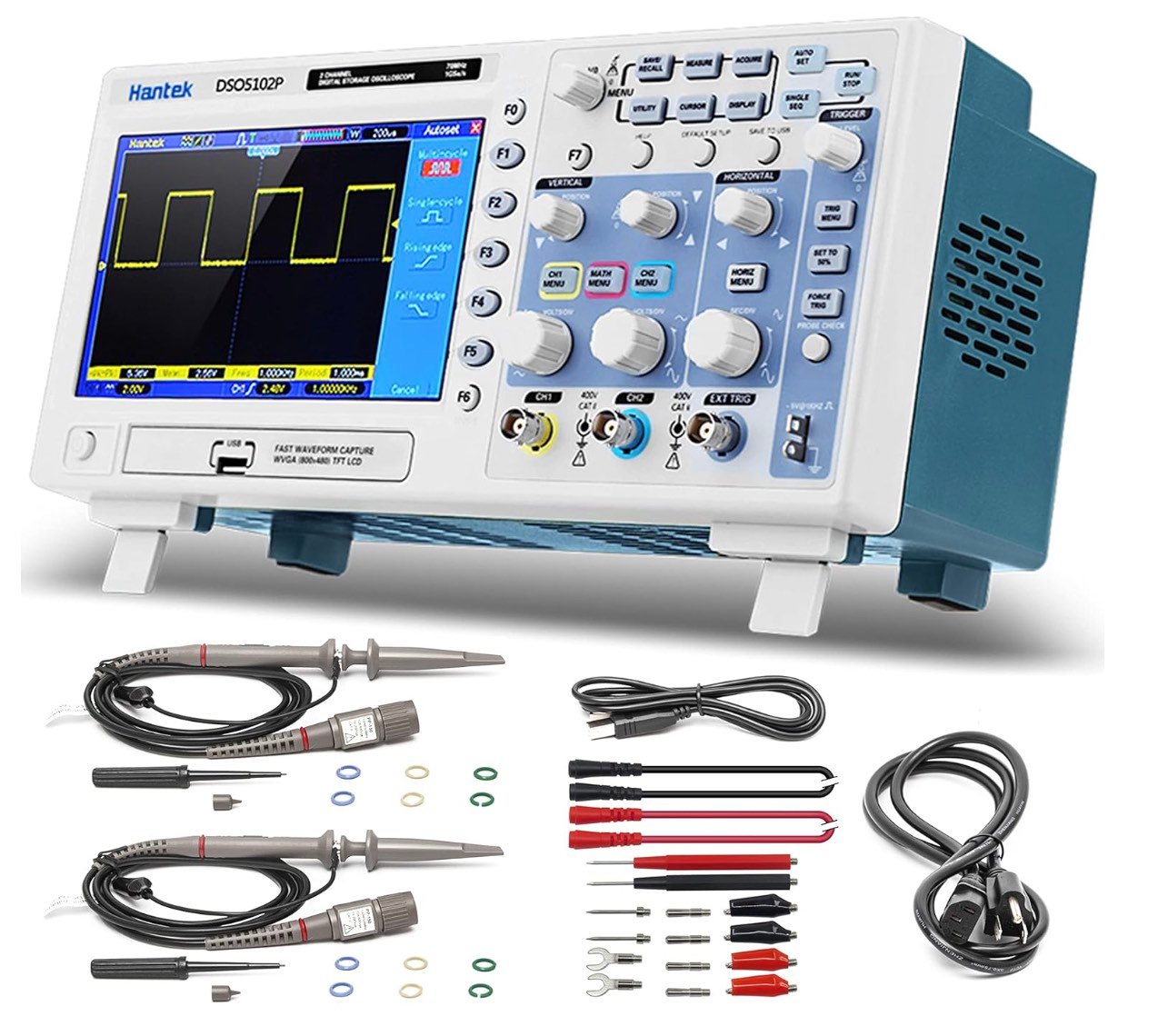
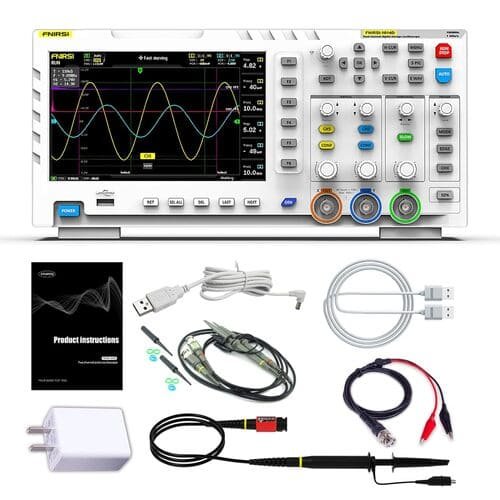
A good beginner choice is the FNIRSI 1014D Digital Oscilloscope. It is our top pick for beginners at a price of less than $199.
FNIRSI 1014D Digital Oscilloscope
(2 in 1 DDS Signal Generator)

Amazon Review Feedback on Analog vs Digital Oscilloscopes under $179
After experimenting with both analog and digital oscilloscopes in the sub-$179 range, it’s clear that each type has its strengths for different applications. Analog oscilloscopes in this price bracket offer real-time display with zero latency, making them excellent for observing fast-changing signals and capturing rare events. They provide a more intuitive feel for signal behavior and are often preferred for educational purposes due to their straightforward operation. However, their measurement accuracy and feature set are limited compared to their digital counterparts. Digital oscilloscopes, even at this budget-friendly price point, offer superior functionality with features like waveform storage, automated measurements, and more precise voltage and time readings. They excel in capturing single-shot events and allow for post-acquisition analysis. Many digital models in this range also offer basic FFT analysis and multiple trigger options. The downside is potential missed events due to dead time between acquisitions. Both types have models with bandwidths typically ranging from 20MHz to 100MHz in this price category. While analog scopes are becoming less common, they still hold value for specific uses. Ultimately, the choice between analog and digital depends on the user’s specific needs, with digital oscilloscopes generally offering more versatility and features for the price in today’s market.
Final Comments
To summarize, analog oscilloscopes represent signals as continuous waveforms on a cathode-ray tube, offering real-time visualization with smooth transitions. In contrast, digital oscilloscopes convert signals into discrete digital values for processing and display on a digital screen, providing advanced features like signal analysis and storage. Digital scopes offer greater accuracy, versatility, and the ability to capture and analyze complex signals compared to analog counterparts.